We recently sat down with enVista’s Tom Stretar and asked him to share some of the most frequently asked questions he and his team receive about Labor Management Systems (LMS). Those questions are presented below, as are Tom’s insightful answers.
What is a Labor Management System (LMS)?
A: An LMS is a supply chain execution program that:
- Defines the best way to perform a task using Lean principles
- Calculates the expected time a task should take
- Provides real-time feedback
- Measures and reports effectiveness
Why should companies consider an LMS project?
A: Organizations, such as distribution centers or stores, typically
operate at 60 to 70 percent of their potential without an LMS.
The reasons for this include: Metrics are not in alignment with company expectations There is a lack of clear expectations for the supervisors and employees Performance feedback is not timely, which prevents immediate corrective action from taking place Lack of formal employee and supervisor change management training
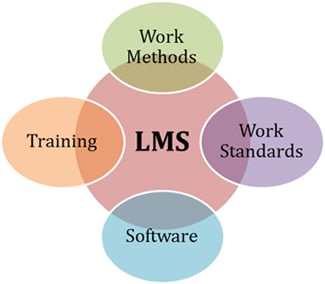
Q: What are the main components of a labor management project?
A: Preferred work methods, work standards, program training and LMS software.
- Preferred Work Methods (PWM): PWMs describe in detail how to best perform a task as opposed to a Standard Operating Procedures that defines what to do. The PWM is the basis for the employee training program.
- Work Standards: These are the expectations, or goals, that are developed in conjunction with the PWMs. Work standards are determined in one of three ways:
- Reasonable expectations – based on the historical average of the volume of units divided by the total number of hours to produce the work
- Multi-variable standards – an engineered approach that takes into consideration multiple factors such as lines, units, cube and weight to determine the time necessary to complete a task
- Discrete engineering standards – this is the most accurate form of an engineered labor standard; it takes into consideration equipment used, actual travel distances, and actual product sizes
- Program Training: This typically consists of change management training, employee observation training in the usage of preferred methods, employee coaching and counseling, and LMS software application end user training. This component of the LMS program is the most crucial in ensuring project success and ongoing sustainability.
- LMS Software: The LMS software provides visibility to the opportunity through the following means:
- Calculation of the expected goal time based on the quantity of work to be performed and the engineered labor standards
- Provides near real-time feedback of comparison of the actual time to the calculated time
- Standardized reporting
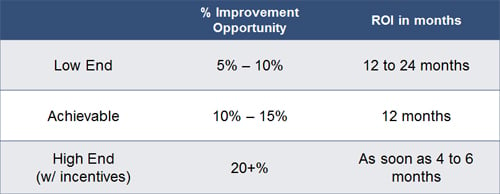
Q: What is the typical Return on Investment (ROI) of an LMS Project?
A: The ROI on an LMS project is dependent upon the type of
engineered standards that are implemented.
The following table represents the three ranges of savings opportunities.
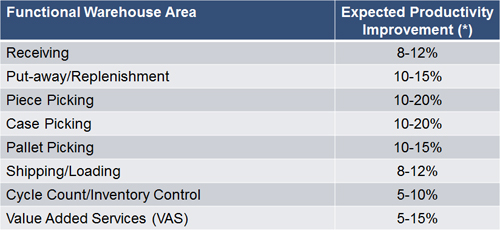
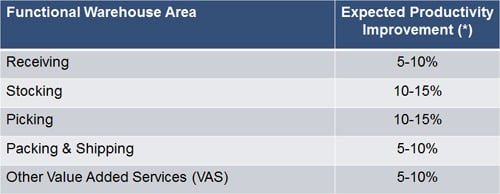
The typical improvement opportunity by DC and Store task types are shown in the tables below.
Expected DC Productivity Improvement
Expected DC Productivity Improvement
Q: What is typical profile of a company that should consider an LMS?
A: Organizations with a payroll of $2 million or more and/or a
minimum of 50 full time employees.
These organizations should consider an LMS to improve productivity and reduce overall supply chain costs. Other common factors include:
- High seasonal workforce usage (i.e., temporary workers for peak holiday season)
- High turnover
- An inexperienced workforce
- A greenfield facility
- Large investments in material handling equipment (forklifts, pallets jacks, turret trucks, or order/stock pickers)
- Considering an incentive plan
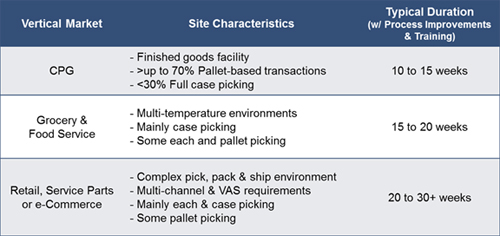
Q: How long does it take to implement an LMS?
A: The answer depends on the type of standards that are developed
and the vertical market of the company.
For facilities employing discrete engineered standards, the typical duration is dependent on the vertical market, as shown in the chart below.
To learn more about labor management system (LMS) selection and implementation, read our white paper.






